
Addition of Ethyl Acetoacetate to Benzene: A Detailed Exploration
The reaction between ethyl acetoacetate and benzene is a fascinating chemical process that has intrigued scientists for years. This article delves into the intricacies of this reaction, exploring its mechanism, applications, and the factors that influence its outcome.
Understanding Ethyl Acetoacetate
Ethyl acetoacetate, with the chemical formula C4H6O3, is an organic compound belonging to the ketone family. It is a colorless liquid with a sweet, fruity odor. Ethyl acetoacetate is commonly used as a solvent in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, perfumery, and plastics.
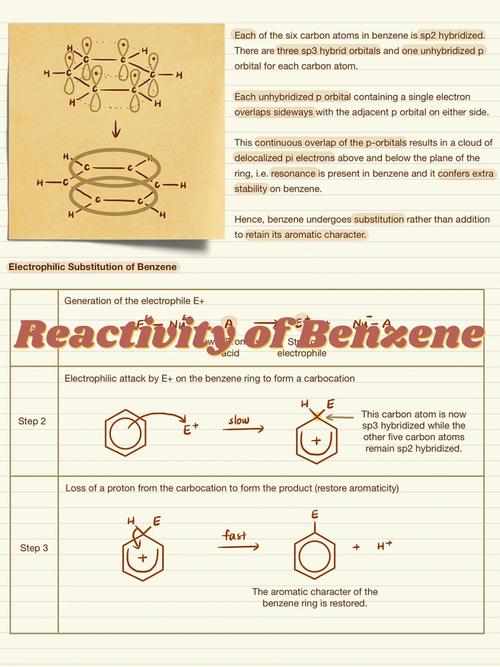
The Benzene Compound
Benzene, with the chemical formula C6H6, is a cyclic hydrocarbon with a hexagonal ring structure. It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic sweet smell. Benzene is widely used as a solvent and as a starting material for the synthesis of various chemicals, including plastics, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
The Reaction Mechanism
The reaction between ethyl acetoacetate and benzene is a nucleophilic addition reaction. In this reaction, the ethyl acetoacetate molecule acts as the nucleophile, attacking the benzene ring. The mechanism of this reaction can be summarized as follows:
- The ethyl acetoacetate molecule donates a pair of electrons to the benzene ring, forming a new bond between the carbon atom of ethyl acetoacetate and the carbon atom of benzene.
- This results in the formation of a new compound, ethyl benzyl ketone, and the release of a molecule of ethanoic acid (acetic acid).
The overall reaction can be represented as:
| Reactants | Products |
|---|---|
| Ethyl acetoacetate + Benzene | Ethyl benzyl ketone + Ethanoic acid |
Factors Influencing the Reaction
Several factors can influence the outcome of the reaction between ethyl acetoacetate and benzene. These include:

- Concentration of Reactants: Increasing the concentration of either ethyl acetoacetate or benzene can increase the rate of the reaction.
- Temperature: Raising the temperature can also increase the rate of the reaction, as it provides more energy for the reactant molecules to collide and react.
- Presence of Catalysts: Catalysts can be used to speed up the reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy.
Applications of the Reaction
The reaction between ethyl acetoacetate and benzene has several practical applications. Some of these include:
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Ethyl benzyl ketone, a product of this reaction, is used in the synthesis of certain pharmaceuticals.
- Plastics Industry: The reaction can be used to produce various plastics, including polyethylene and polypropylene.
- Perfumery: Ethyl benzyl ketone is used in the production of perfumes and fragrances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the reaction between ethyl acetoacetate and benzene is a significant chemical process with a variety of applications. Understanding the mechanism and factors influencing this reaction can help scientists and engineers optimize the reaction conditions and improve the efficiency of the process.





