
Understanding the Base ETH Address: A Comprehensive Guide
Embarking on the journey of understanding the base ETH address is akin to unraveling the mysteries of the Ethereum blockchain. As you delve deeper, you’ll discover a world where digital currencies and smart contracts coexist, creating a new paradigm for financial transactions and decentralized applications. Let’s dive into the intricacies of the base ETH address, exploring its significance, functionalities, and the ecosystem surrounding it.
What is a Base ETH Address?
A base ETH address is a unique identifier for an Ethereum account. It is a 42-character hexadecimal string that starts with ‘0x’ followed by 40 alphanumeric characters. This address serves as the gateway to interact with the Ethereum network, allowing users to send, receive, and store Ether (ETH), the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum platform.

Structure of a Base ETH Address
The structure of a base ETH address can be broken down into three main components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| 0x | Prefix indicating that the address is a hexadecimal value. |
| 40 Alphanumeric Characters | Unique identifier for the Ethereum account. |
These 40 characters are generated using the Keccak-256 hashing algorithm, which ensures the uniqueness and security of each address. The combination of these characters creates a 160-bit address, making it impossible for two addresses to be identical.
Creating a Base ETH Address
Creating a base ETH address involves generating a private key, which is a 64-character hexadecimal string. This private key is then used to derive the public key, which is a 128-character hexadecimal string. Finally, the public key is hashed using the Keccak-256 algorithm to obtain the base ETH address.
Interacting with a Base ETH Address
Once you have a base ETH address, you can interact with it in various ways:
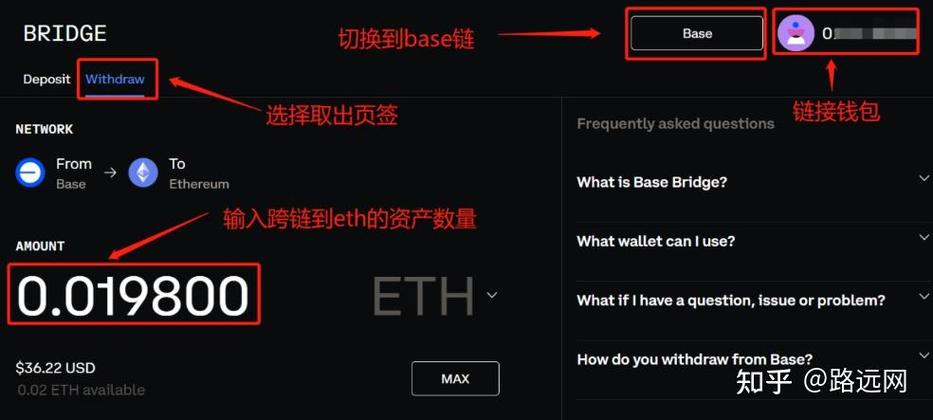
-
Receiving ETH: You can receive ETH by providing your base ETH address to others who wish to send you funds.
-
Sending ETH: To send ETH, you need to have a private key associated with your base ETH address. By using this private key, you can sign a transaction that transfers ETH from your account to another address.
-
Storing ETH: You can store ETH in your base ETH address by simply holding it. The funds will remain in your address until you decide to send or withdraw them.
Security Considerations
Security is paramount when dealing with base ETH addresses. Here are some key considerations:
-
Private Key Protection: The private key is the key to your base ETH address. If someone gains access to your private key, they can control your funds. Therefore, it is crucial to keep your private key secure and never share it with anyone.
-
Backup: Create backups of your private key and store them in multiple secure locations. This ensures that you can recover your funds in case of loss or damage to your primary storage device.
-
Phishing Attacks: Be cautious of phishing attacks that attempt to steal your private key. Always verify the authenticity of websites and emails before providing any sensitive information.
The Ecosystem Surrounding Base ETH Addresses
The base ETH address is not just a standalone entity; it is an integral part of the broader Ethereum ecosystem. Here are some key aspects of this ecosystem:
-
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They are deployed on the Ethereum network and can be accessed using base ETH addresses.
-
DApps: Decentralized applications (DApps) are applications built on the Ethereum platform. They utilize base ETH addresses for user authentication, transactions, and other functionalities.
-
Exchanges and Wallets: Exchanges and wallets are platforms that facilitate the buying, selling, and storing of ETH. They often require users to provide their base



