
Understanding and Configuring DNS for Your Ethernet Network
Managing your network’s DNS settings is crucial for ensuring smooth and secure internet connectivity. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of DNS (Domain Name System) and how it relates to your Ethernet network. Whether you’re a tech-savvy user or just starting out, this guide will help you navigate the world of DNS with confidence.
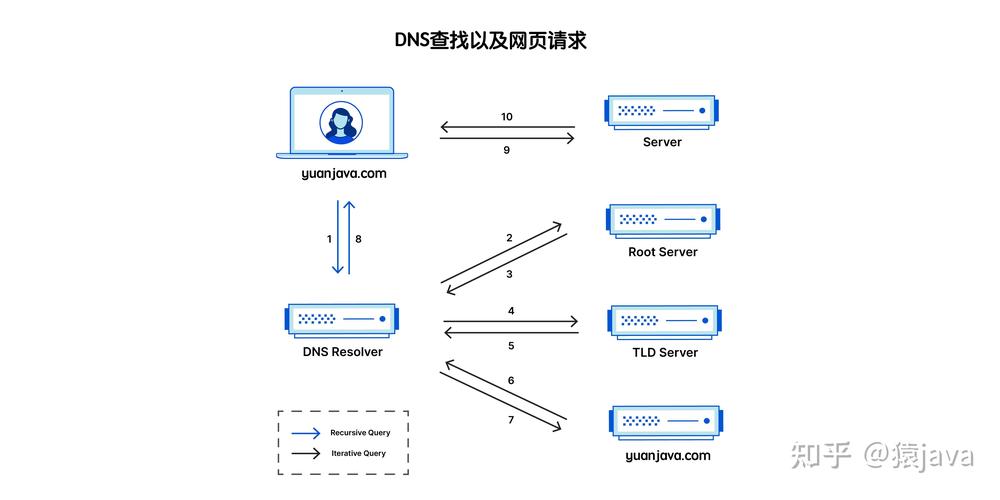
What is DNS?
DNS is like a phonebook for the internet. It translates human-readable domain names (like www.example.com) into IP addresses (like 192.168.1.1) that computers use to communicate with each other. When you type a domain name into your web browser, your computer sends a DNS query to a DNS server to find the corresponding IP address.
Understanding Ethernet and DNS
Ethernet is a common networking technology that allows devices to connect to a local network or the internet. Your Ethernet network may consist of multiple devices, such as computers, smartphones, and smart home devices. Each of these devices needs to know how to find and communicate with other devices on the network, which is where DNS comes into play.
Configuring DNS for Your Ethernet Network
Configuring DNS for your Ethernet network involves several steps. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
-
Access Your Router’s Configuration Page
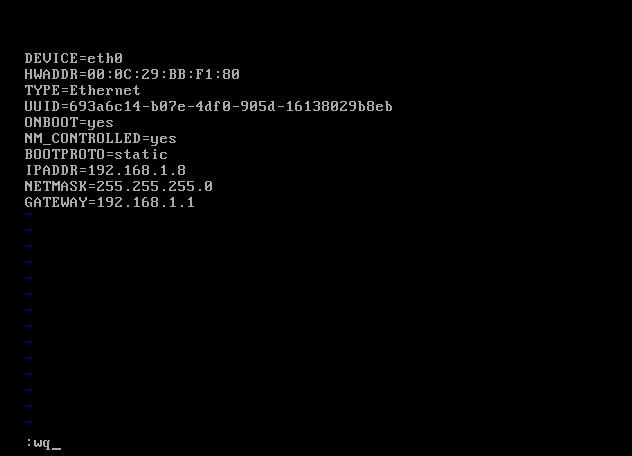
-
Locate the DNS Settings
-
Enter the DNS Server Addresses
-
Save and Apply the Changes
Here’s a table showing some popular DNS server addresses:
| DNS Server | IP Address |
|---|---|
| Google Public DNS | 8.8.8.8 |
| Cloudflare DNS | 1.1.1.1 |
| OpenDNS FamilyShield | 208.67.222.222 |
Using DNS to Improve Network Performance
Configuring your DNS settings can also help improve your network’s performance. Here are a few ways to do that:
-
Use a Local DNS Cache
-
Configure DNS Load Balancing
-
Implement DNSSEC for Security
Common DNS Issues and Solutions
Even with the best DNS settings, you may encounter issues from time to time. Here are some common DNS problems and their solutions:
-
DNS Server Not Responding
Check your internet connection, restart your router, or try using a different DNS server.
-
Domain Name Not Found
Ensure that the domain name is spelled correctly and that the website is online.
-
Slow DNS Resolution
Try using a different DNS server or configure a local DNS cache.
Conclusion
Understanding and configuring DNS for your Ethernet network is essential for ensuring reliable and secure internet connectivity. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can optimize your DNS settings and improve your network’s performance. Remember to keep your DNS settings up to date and monitor for any potential issues to maintain a smooth and efficient network experience.




