
ADSL, ATM, and ETH: A Comprehensive Comparison
When it comes to internet connectivity, understanding the differences between various technologies is crucial. Two popular technologies that have been widely used are ADSL and ATM, while ETH, or Ethernet, has gained popularity in recent years. In this article, we will delve into the details of these technologies, comparing their features, performance, and applications.
What is ADSL?
ADSL, which stands for Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line, is a type of internet connection that uses existing copper telephone lines to provide high-speed internet access. The key feature of ADSL is its asymmetric nature, meaning that the upload and download speeds are not equal. Typically, ADSL offers higher download speeds than upload speeds, making it ideal for activities like web browsing and streaming.
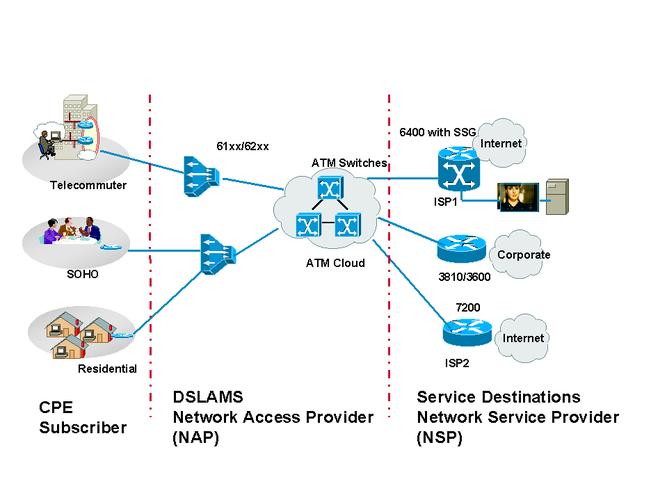
What is ATM?
ATM, or Asynchronous Transfer Mode, is a switching technology that was developed in the 1980s. It is designed to handle a wide range of data types, including voice, video, and data, over a single network. ATM uses fixed-size cells to transmit data, which allows for efficient and reliable communication. This technology is commonly used in telecommunications networks and data centers.
What is ETH?
ETH, or Ethernet, is a family of computer networking technologies that are widely used for local area networks (LANs). It provides a reliable and high-speed connection between devices within a limited geographic area. Ethernet uses a variety of cables, including copper and fiber optic, to transmit data. It is known for its scalability and ease of use, making it a popular choice for both home and business networks.
Performance Comparison
Now that we have a basic understanding of these technologies, let’s compare their performance in terms of speed, latency, and reliability.
Speed
ADSL speeds typically range from 1.5 to 8 Mbps for downstream and 0.5 to 1 Mbps for upstream. While this may be sufficient for basic internet activities, it may not be ideal for high-bandwidth applications like streaming 4K video or online gaming.
ATM speeds can vary depending on the network configuration, but they generally range from 155 Mbps to 622 Mbps. This makes ATM a suitable choice for high-speed data transmission in telecommunications networks and data centers.
ETH speeds can vary widely, with standard Ethernet offering speeds of up to 1 Gbps, while Gigabit Ethernet can provide speeds of up to 10 Gbps. This makes ETH an excellent choice for both home and business networks, especially for applications that require high bandwidth.
Latency
ADSL latency is generally higher than that of ATM and ETH, which can be a concern for real-time applications like video conferencing and online gaming.
ATM latency is relatively low, making it suitable for time-sensitive applications. However, the actual latency can vary depending on the network configuration and the distance between the sender and receiver.
ETH latency is also low, with standard Ethernet offering latency of around 1 millisecond. This makes ETH an excellent choice for real-time applications and high-performance computing.
Reliability
ADSL is generally considered to be a reliable technology, but it may experience issues with signal quality and interference, especially over longer distances.
ATM is known for its high reliability, as it uses fixed-size cells to ensure that data is transmitted without errors. This makes ATM a suitable choice for critical applications that require a high level of reliability.
ETH is also a reliable technology, with standard Ethernet offering a high level of error detection and correction. This makes ETH a suitable choice for both home and business networks.
Applications
Now that we have compared the performance of these technologies, let’s explore their applications in different scenarios.
ADSL
ADSL is commonly used for home and small business internet connections, as it provides a cost-effective solution for basic internet access. It is also used in rural areas where other high-speed internet options may not be available.
ATM
ATM is primarily used in telecommunications networks and data centers, where high-speed and reliable data transmission is critical. It is also used in financial institutions for secure and efficient data transfer.
ETH
ETH is widely used in both home and business networks, as it provides a reliable and high-speed connection between devices. It is also used in data centers, where high-performance computing and real-time applications are common.




